TEXT
There are three key facts about Canada’s system of government: it is a constitutional monarchy, a parliamentary democracy and a federal state.
Federal state
Canada has three levels of government – federal, provincial or territorial, and municipal. Each level of government has different responsibilities and a different role to play in the country.
Federal government
The federal government is based in Ottawa, the capital city of Canada. It is responsible for national and international matters, such as national defence, foreign affairs, Employment Insurance, currency, banking, federal taxes, postal services, shipping, railways, telephones and pipelines, Aboriginal lands and rights, and criminal law. In general, the federal government deals with laws that affect the whole country.
The federal government is led by the Prime Minister who is the most senior or “first” minister in the government. Provincial and territorial governments.
Provincial and territorial governments.
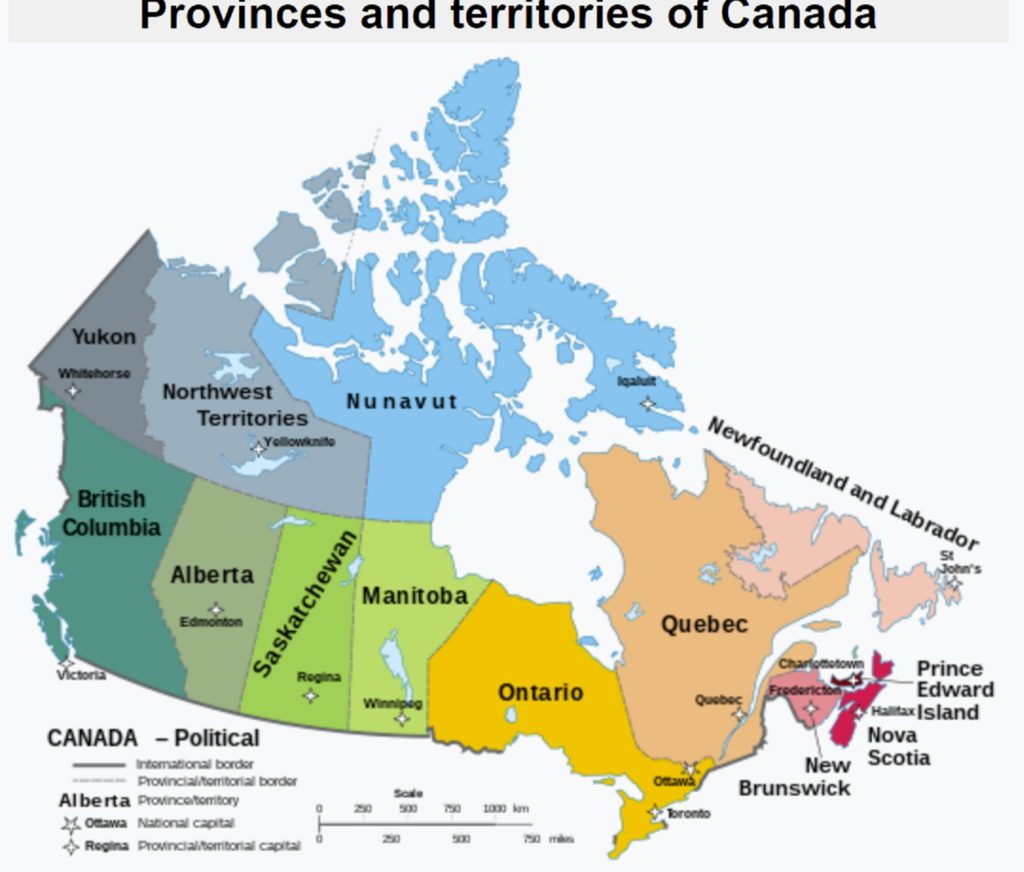
There are 10 provinces and three territories in Canada. Each province is led by a Premier and has its own elected legislature. It has the power to change its laws and manage its own public lands. Each of the territories is also led by a Premier and carries out many of the same functions as a province, but the federal government manages the public lands.
In each of the 10 provinces in Canada, the provincial government has a variety of responsibilities identified in the Constitution Act, 1867. These include education, health care and road regulations. Provincial governments sometimes share responsibilities with the federal government. For example, federal and provincial governments share power over agriculture, natural resources and immigration.
Municipal governments
This is the level of government that governs a city, town or district (a municipality).
Municipal governments are responsible for areas such as public transportation, fire protection, local police, local land use, libraries, parks, community water systems, roadways and parking. They receive authority for these areas from the provincial governments. Municipal governments are led by a mayor.
First Nations governance
Across the country there are also band councils that govern First Nations communities. Band councils are similar to municipal governments; the members of a band elect the band council, which makes decisions that affect their local community.
Parliamentary democracy
Parliament has three parts: the Sovereign (Queen or King), the Senate and the House of Commons. In Canada’s parliamentary democracy, the people elect representatives to the federal House of Commons in Ottawa. The people also elect representatives to provincial and territorial legislatures as well as to their city council. These representatives are responsible for passing laws, approving and monitoring spending, and keeping the government accountable.
Normally the party that has the most elected members is asked by the Governor General (Federal level) or Lieutenant Governor (Provincial level) to form the Government.
At the municipal level, the mayor is elected independently of the councilors.
Relation between the different levels of government:
Each level of government is politically independent of the others. It collects its own taxes, manages its own budgets, and appoints its own civil servants.
The Premiers and the Prime Minister appoint ministers to their cabinets to help them govern. Ministers are chosen among the elected members of parliament. Mayors don’t have cabinets and rely on civil servants to do their jobs.
Most municipalities have their own police force to enforce their bylaws. Provincial Police or the Federal Police are called only when there are major crimes, such as homicides. Some municipalities, especially smaller ones may leave policing entirely to the Provincial Police or Federal Police.
Differences with the US:
The US elects some positions that are appointed in Canada, such as the Sheriff (Police Chief), the Attorney General (Government Prosecutor).
RELATED LINKS
EXPRESSIONS
Could turn either way: Could be a win for one party or the other.
Hang on: 1. Cling to the position 2. Wait a short time. 3. Listen attentively
Grind that agenda to a halt: To stop it
Use the veto pen: Use the power to refuse (The US President has the power to refuse a law approved by Congress. Congress can override this power by a majority of 2/3.
GRAMMAR
Noun compounds
Complete the following sentences with a noun compound formed by the two italicized nouns. The compounds consist of one word or two, as shown by the blanks.
Rules: Open, closed, or hyphenated
Examples: A small boat saved his life. It was a lifeboat.
The streetlights were off, but he could see by the light of the moon. The street was lit up by the moonlight.
He raises chickens on his farm. He has a chicken farm.
1. He deposited the mail in the box. He put the letters in the — mailbox –.
2. The man holding the door is the — doorman –.
3. He went into the store to buy some shoes. He went into the — shoestore –.
4. She drank some tea from the cup. She drank from the — teacup –.
5. Just throw any waste paper in this basket. It’s a — wastebasket –.
6. That man has the highest sales record. He’s the best — saleman –. in the
company.
7. Mary bought a shade for the lamp. She bought a — lampshade –.
8. He likes to go sailing in his boat. He has a — sailboat –.
9. Her watch fell off her wrist. She lost her — wristwatch –.
10. This store has a number of different departments. It’s a — department store –.
11. The bells of the church rang out. I heard the — church bells –.–.
12. We need some more wax for this floor. We need some — floor wax –.
13. She was carrying the hat in a box. She was carrying a — hatbox –.
14. He gave her a ring for their engagement. He gave her an — engagement ring –.
15. Does that train carry passengers? Yes, it’s a — passenger train –.
16. I got these books from the library. These are — library books –.
17. Mr. Evans bought a collar for his dog. He bought a — dog collar –.
18. This paper appears in the evening. It’s an — evening paper –.
19. You wear these shoes when you go bowling. These are — bowling shoes —
20. I can’t fasten this button for my collar. Please help with — collar button –.
21. I need a coat to wear in the rain. I’ll have to buy a — raincoat –.
22. Do you have a list of your prices? I’d like to see your — price list –.
SPEAKING PRACTICE
Talk about an election system that you know.